Persistence Vault
The persistence vault is the persistent layer where data is stored. Amongst it's roles and responsibilities:
- The persistent store implementation is one of the ones supported by GORM
- Terminus ships by default with a PostgreSQL data store
- Supports multi-tenancy and multi-product logical segregation via column keys
- All data is encrypted and there is no indication of what the data stored is
- It exposes the low-level API for the Proxy to interface with the persistence
- Can implement additional encryption at rest if supported by the store implementation
- It is not business model aware
- It's scalability, partitioning and indexing capabilities is directly depending on the choice of store
It is written in Go.
Interaction with the Persistence Vault
Leverages GORM to interface with the database. Currently is configured to use PostgreSQL but supports any persistence store supported by GORM.
Implements AES encryption against the data store.
⚠️ IMPORTANT: changes on encryption keys of the logical encryption layer will render the data stored useless.
Configuration
The specific configuration depends on the data store.
By default it is PostgreSQL and gets configured via Docker Compose and environment variables.
Schema
Terminus' schema is transparently deployed by the Vault Service layer via GORM
It comprises one data table with the following structure:
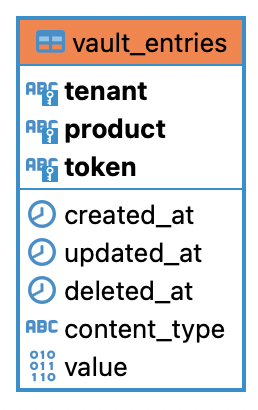
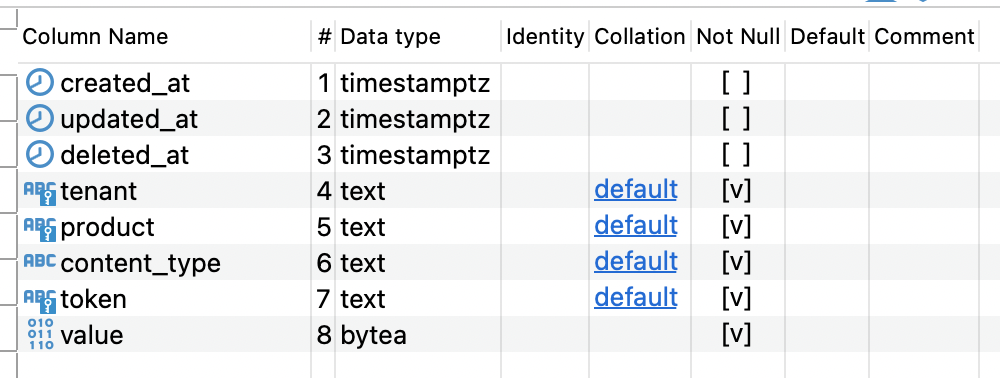
With:
tokenbeing the entry identifier (it's the ID that gets returned on creation and is required for retrieval)valuebeing where the data is stored transparentlycontent_typebeing the mime-type of the stored data for retrieval (json, xml, binary, etc.)tenant,productbeing the keys for multitenancy indicating Terminus' customer and the configured product